Accueil > Equidae monodactyles > Equidés monodactyles fossiles (Equus, Allohippus, (…) > Amérique du Nord, Amerhippus
Amerhippus occidentalis
Rancho La Brea et MacKittrick, Californie : E. occidentalis
E. occidentalis, Leidy, 1865, Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci., 94. California. “Types†are from Tuolumne Co. (aurifere deposits) and tars of Buena Vista Lake.
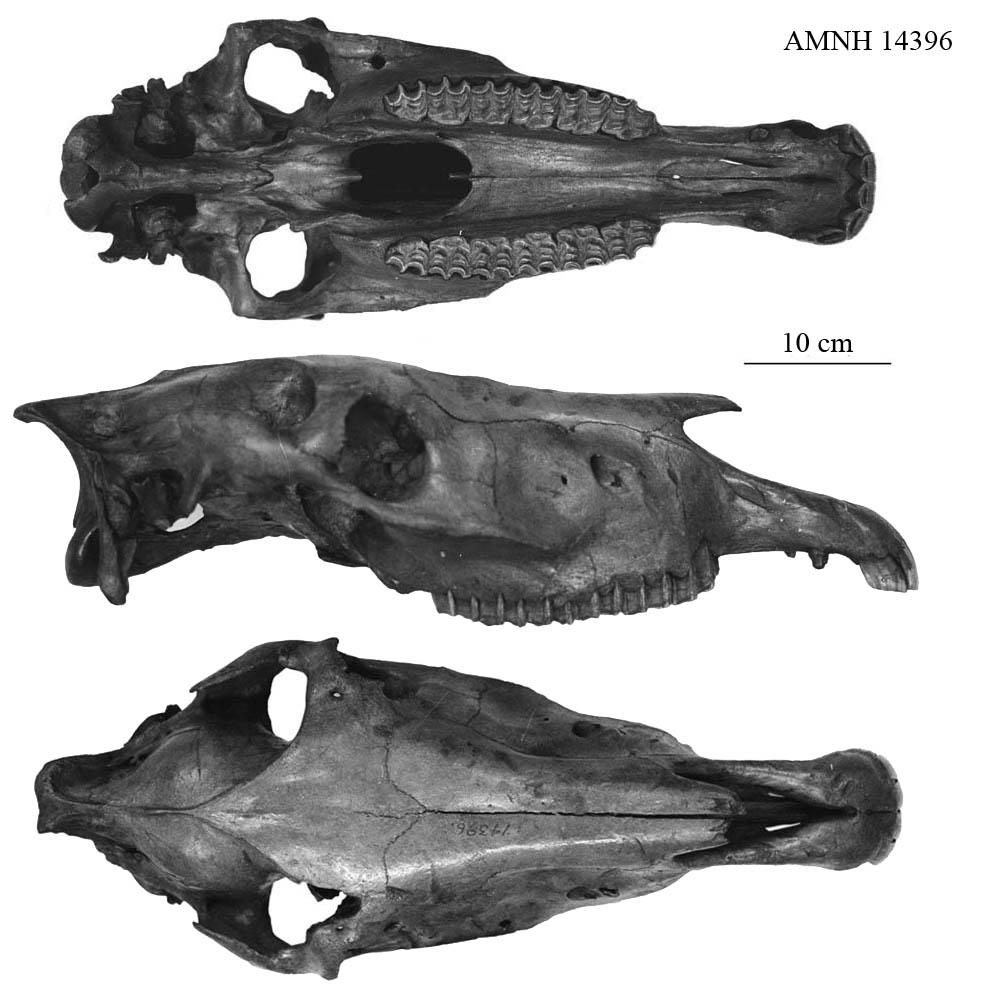
SKULL
Fig.1 - Cranium of A. occidentalis, AMNH 14396, Rancho La Brea.
The size is about that of the E. grevyi - largest among the extant species. It differs from all of them by its muzzle, frontal, and choanal widths (Fig.2, 17 ; 17bis ; 13 ; 10) and its depths (25 ; 28).
– Because of the backwards development of the occiput, the vertex length relative to the basilar is longer than in Caballines. It is the usual pattern in all Zebras and other Amerhippus (Fig.3).
– For the same reason, the post-ocular line is longer than the preorbital line than in Caballines. The proportions are like in E. burchelli and E. africanus (Fig.4).
– The cheek length is long relative to the depth of tha naso-incisive notch, longer than in most Caballines and close to the other extant Equus and Amerhippus (Fig.5).
– The basilar proportions are not caballine (Fig.6).
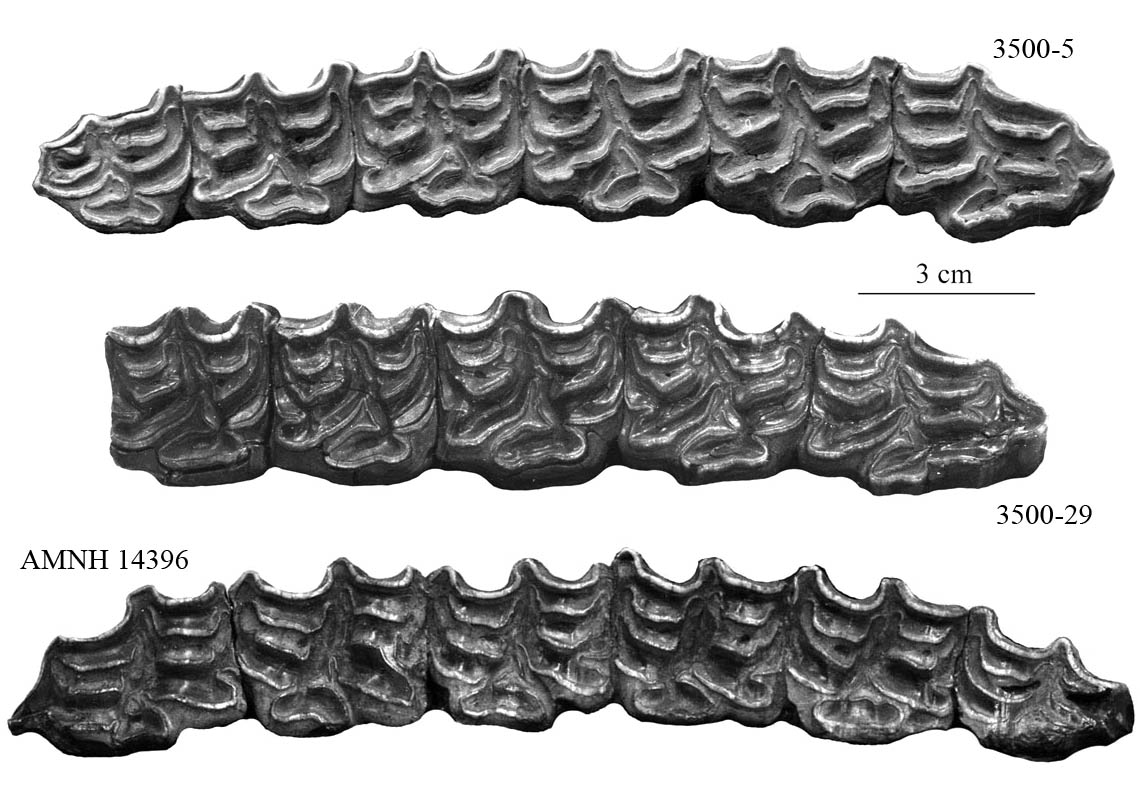
UPPER CHEEK TEETH
Meso and metastyles are not grooved. The enamel is simple.
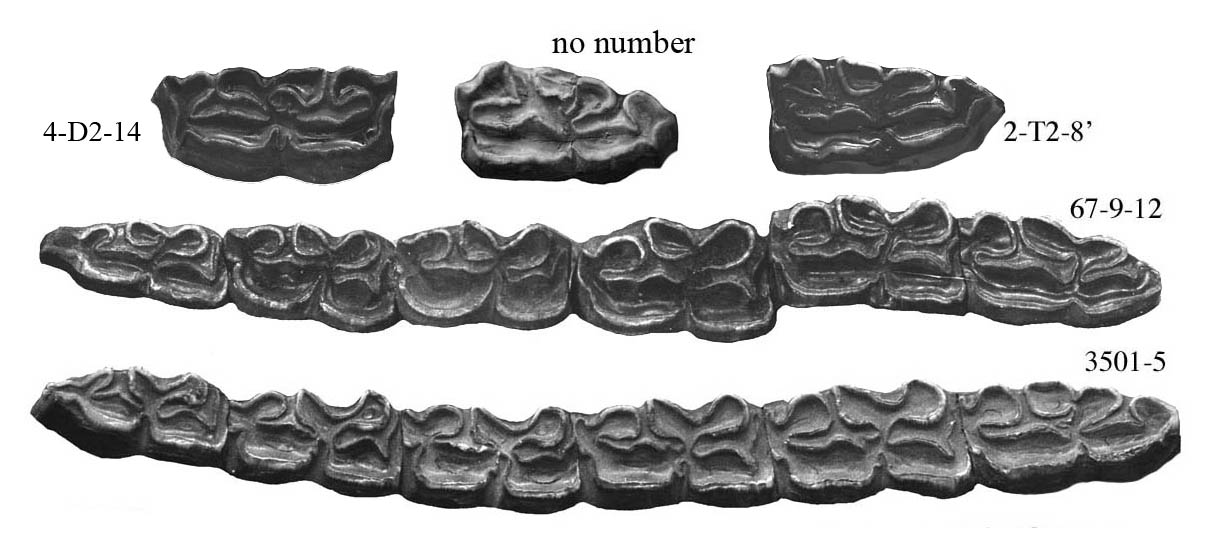
Post-protocones valleys tend to be deeply invaginated (Fig.7, P4 of 3500-29) but may yet include plis caballin (P3 of 3500-29) Plis caballin seem frequent on P2 (Fig.7).
Protocones are assymetric, long, wide, and bumped.
LOWER CHEEK TEETH
Double knot usually symetric with round metaconid and metastylid. No penetration of the isthmus by the vestibular groove (Fig.8).
Plis protostylid on P2 are rare but occur ; they seem more frequent on dP2.
Some worn molars are caballoid (3501-5) but the lingual groove is rounded, shallow, not as in the true caballine pattern.
INCISIVES
The lower incisors have no cups (Fig.9).
LIMB BONES
All are very large. The limb segments proportions are not unlike those of E. zebra (Fig.10).
Metacarpals have deep proximal ends (Fig.11 ; 6) and wider articular distal than supra-articular ends (Fig.11 ; 11 and 10). Metatarsals have the same distal proportions bur they tend to have relatively wide proximal ends.
First phalanges are not unlike those of E. zebra and E. burchelli (Fig.12).